Green Bond Market Guide
The clean-energy transition and the drive to create a more inclusive society are transforming the global economy. With climate change continuing to affect companies and communities around the world, a successful transition to a low-carbon economy is more important than ever. This decarbonization push will require changes across the economy, especially in high-emitting sectors such as agriculture, construction, heavy industry and transport.
The global bond market will be an important source of investment to drive the climate transition. Yet until recently, investors seeking to reduce the carbon footprint of their fixed income portfolios had few options. The rapid growth of the green bond market – 43% per year from 2016 through 2023 – has changed that.1
Once a niche product, these bonds that finance environmentally beneficial projects and programs have expanded into a $2.5 trillion market.2 We believe this expansion and the widening range of mutual and exchange-traded funds offering exposure to green bonds have made them a viable complement to existing fixed income allocations, subject to investors’ risk tolerance and investment objectives, that offers a potentially positive contribution to the global push to manage the impact of climate change.

Source: Goldman Sachs Asset Management, Bloomberg. Data as of December 31, 2023. For illustrative purposes only.
What Are Green Bonds?
Green bonds are standard fixed income securities with a green goal. Their financial characteristics such as structure, risk and return are similar to those of traditional bonds from the same issuer. They range from investment grade to non-investment grade, though most corporate green bonds are investment grade. Like traditional bonds, green bonds come in short- or long-dated maturities and have various coupons and yields.
The main difference is that the goal for green bonds is to finance only projects or activities with a specific environmental purpose such as renewable energy, clean transportation, sustainable water and energy efficiency. This commitment to advancing the climate transition goes back to the first green bond, issued in 2007 by the European Investment Bank (EIB).3
Dominated in the early years by multilateral development banks such as the EIB and the World Bank, which issued its first green bond in 2008,4 the market has seen the range of issuers expand to include companies and governments across the globe seeking investment to drive their plans to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and manage physical climate risks. The investor base has also expanded to include a growing number of traditional fixed income investors, not just those focused primarily on impact and sustainability criteria.
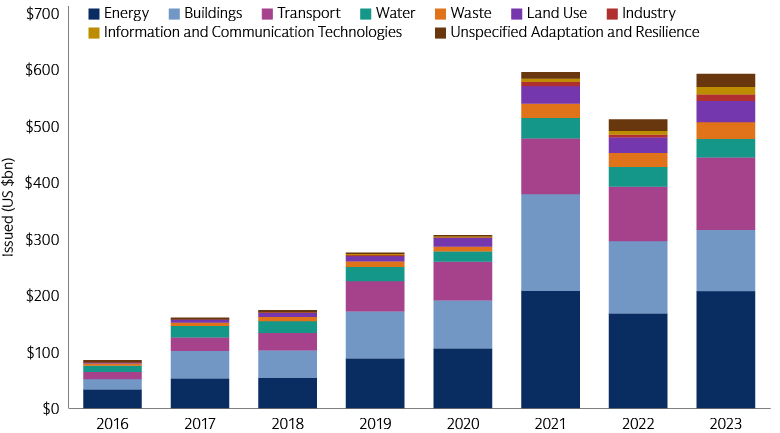
Source: Climate Bonds Initiative. Data as of December 31, 2023.
Green Bond Market Guide
Goldman Sachs Asset Management’s Green Bond Market Guide provides a comprehensive introduction to this market. Its first section is devoted to an explanation of what green bonds share with conventional bonds and the features that set them apart. It also explores the voluntary industry standards and regulatory initiatives that have helped enhance the credibility and transparency of the market.
The guide then looks at the history of the green bond market and the global climate initiatives that are spurring the mobilization of capital to finance the climate response. This second section also compares the green bond market with the broader market in terms of performance and composition, providing a detailed view of green bonds’ rapid development. Finally, the guide’s third section lays out the fixed income investment opportunity in green bonds and the value of an active investment approach, which can help investors limit downside risk and uncover the opportunities with the most attractive potential returns.
At Goldman Sachs Asset Management, we are committed to seeking to help investors manage the risks and seize the potential opportunities created by the transition to a low-carbon, more inclusive economy. Our green, social and impact bond funds are some of the solutions we provide to help clients accomplish their sustainability-related objectives. Learn more here.
1 Goldman Sachs Asset Management, Bloomberg. As of December 31, 2023. The growth value provided is the geometric mean covering the years stated.
2 Goldman Sachs Asset Management, Bloomberg. As of June 30, 2024.
3 "EPOS II - The ‘Climate Awareness Bond’: EIB Promotes Climate Protection Via Pan-EU Public Offering," EIB press release. As of May 22, 2007.
4 "World Bank and SEB Partner With Scandinavian Institutional Investors to Finance ‘Green’ Projects," World Bank press release. As of November 6, 2008.

